Massachusetts is a hub for life sciences careers, with companies needing eager students with skills to fill R&D, biomanufacturing, and medical device internships and jobs. In this guide, we delve into the foundational concepts of teaching life sciences in Massachusetts, providing recommendations for practical technologies and equipment to integrate into your program. Discover how to nurture scientific inquiry, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills in your students, preparing them for a future in in-demand STEM fields.
The importance of teaching life sciences in Massachusetts
Life sciences form the foundation of our understanding of the natural world and how living organisms function. Teaching life sciences is crucial as it provides students with the opportunity to explore and appreciate the interconnectedness of all living things. By understanding concepts such as evolution, genetics, and ecology, students gain a deeper appreciation for the diversity of life on Earth for a range of future careers.
In addition, teaching life sciences helps students develop critical thinking skills, problem-solving abilities, and scientific literacy. These skills are essential for future careers in STEM fields and for making informed decisions about health, the environment, and ethical considerations. Incorporating Industry 4.0 training gives students an edge with skills relevant to working in automated biopharma and biotech manufacturing facilities, which are growing in Massachusetts.
Life sciences is a broad discipline that students at any experience level can learn about, from foundational science skills for middle school students to in-depth research at the college level. Example teaching topics include:
Fundamentals of Life Sciences
- The scientific method
- Living organisms
- Life cycles of plants and animals
Life Sciences Concepts
- Cell structure and function
- Human biology
- Ecology
- Evolution
Biomedical Science and Biotechnology
- Human anatomy and physiology
- Cell biology
- Genetics and DNA
- Health and bioethics
Biomanufacturing and Medtech Manufacturing
- Bioprocess engineering
- Cell culture
- Quality control and assurance
- Automation and control systems
In Massachusetts, life sciences careers are in demand. Careers in life sciences are at companies specializing in research and development, commercialization, and manufacturing in biopharma, medical device, diagnostics, and digital health. In 2023, the biopharma R&D workforce experienced year-over-year employment growth of 8.5%, while biomanufacturing grew by 6.3%, for a total growth rate of 6.9%.
Equipment and resources for teaching life sciences
Teaching life sciences requires a combination of traditional and innovative methods to engage students and cater to different learning styles. Incorporating hands-on activities and experiments with equipment replicating the real world allows students to actively explore and discover key concepts.
Additionally, incorporating experimentation and problem-solving activities can foster critical thinking skills and scientific inquiry. Encourage students to ask questions, design experiments, and analyze data to better understand the life sciences.
To enhance your life sciences teaching, it is essential to have access to equipment suitable for the experience level of your students with corresponding curriculum guides and practical activities to engage students and deepen their understanding of life sciences. From exploring human anatomy to running a replica of an automated manufacturing facility, practical experiences from these technologies allow students to apply their life sciences knowledge and develop essential laboratory skills:
For Middle School Students
Students experiment by themselves to experience the basic principles of bionics and scientific work with six exciting experiments.
Introduces students to the basic principles of project work and the fundamentals of closed-loop control without a PC or sophisticated control technology.
Introduces students to various life sciences topics, including life cycles, the five senses, and botany, with an immersive experiential learning platform.
For High School Students
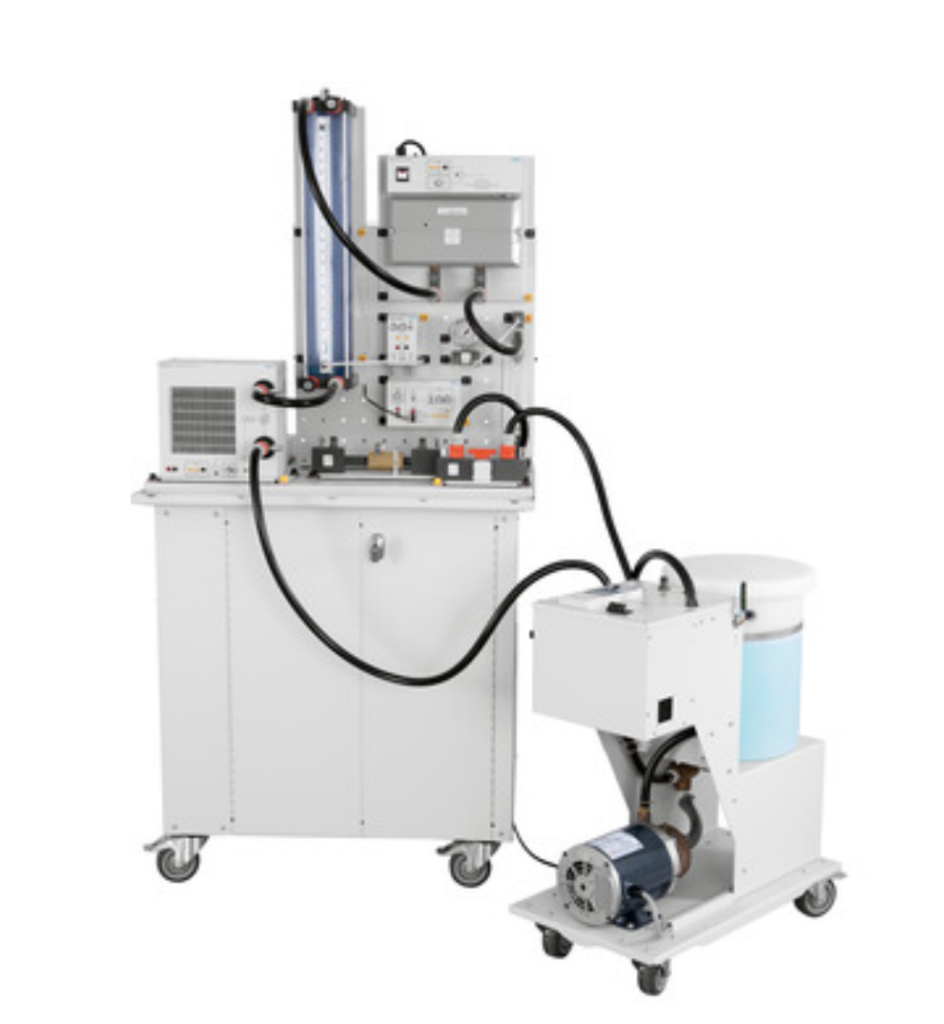
Students learn the fundamentals of PID (proportional, integral, derivative) control of flow, pressure, and level processes in a compact workstation.
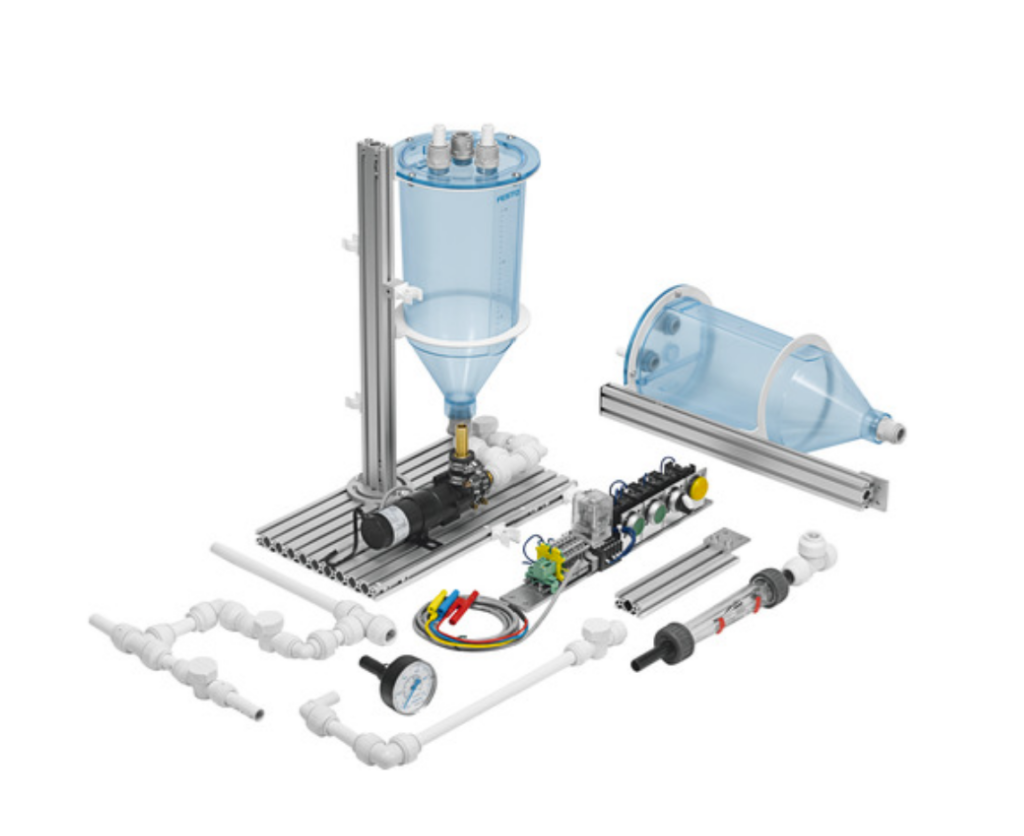
All-in-one process workstation with instrumentation for four process variables measurement.
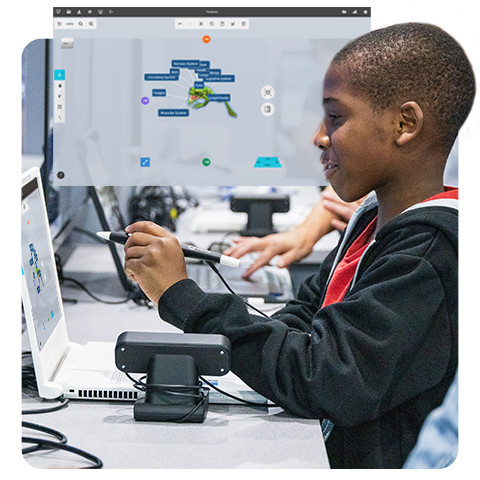
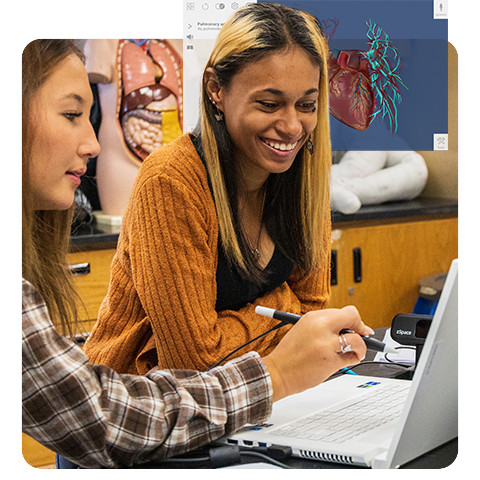
zSpace, an experiential learning platform, helps students get exposure to skills that would typically be difficult to incorporate into a classroom setting, including the human anatomy, biochemistry, cells and viruses, and genetics.
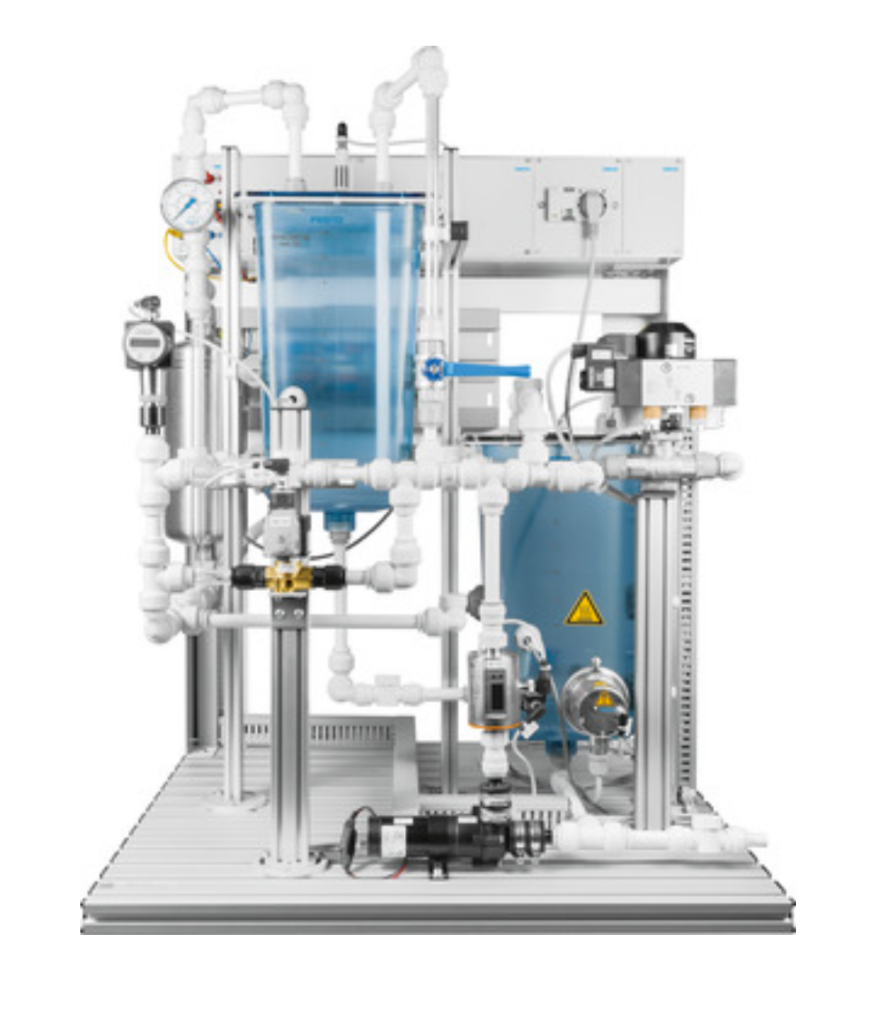
For Post-Secondary Students
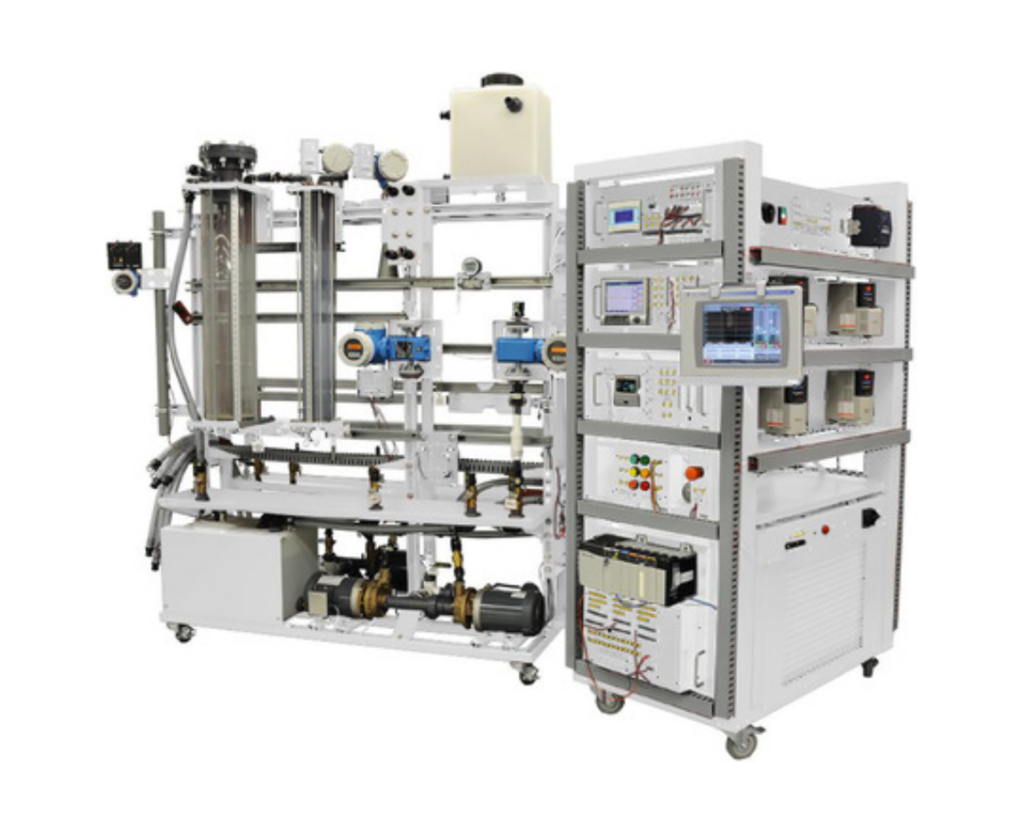
Bring the process plant into your lab with a flexible, industrial training platform that introduces students to pressure, flow, and level processes and associated instruments and control.
Partnering with local companies to bring field trips, real-life examples, guest speakers, case studies, and current scientific research can also help students see the relevance and applications of life sciences in the world around them.
By teaching life sciences to students at any experience level, you can inspire young minds and ignite their passion for biology, playing a vital role in preparing them for a future in growing STEM fields in Massachusetts and contributing to the advancement of scientific knowledge.
Are you ready to explore how to bring life sciences education to your district or higher ed institution? AET Labs is your partner in applying for the Massachusetts Life Sciences Center grants to help you bring the newest technologies to your program. Contact us to get help on your grant application!