Makerspaces have evolved from community spaces for entrepreneurs and hobbyists to engaging environments for students of all ages to gain new skills and explore their interests. If you're looking to create a makerspace for education in New England, we're here to provide you with some helpful makerspace guidelines for getting started.
What is a Makerspace?
Makerspaces are collaborative spaces where people can explore their ideas and get hands-on experiences making things with various equipment and tools.
Many makerspaces were community-driven organizations before schools started adopting the model. As a result, volunteers have always supported the environment to some degree. Because of this, makerspaces lend a welcoming environment to community outreach organizations, local businesses (especially startup incubators), and even robust afterschool and summer camp programs for youth. This cultural aspect often plays a role in academically oriented makerspaces.
We've seen makerspaces in high schools with dedicated spaces or with makerspace areas in the classroom or library. At universities, we've seen makerspaces on campuses that bring students from different schools within the universities together.
Why is a Makerspace Important?
Makerspaces are important because they allow students to build valuable soft and technical skills that benefit them academically and in future career paths. They also give instructors more flexibility to teach in ways that engage students.
Teamwork, problem-solving, and creativity are some of the soft-skills students are exposed to in a makerspace where they collaborate with other students. Project-based learning in makerspaces empowers students to try new things and use their imagination.
Incorporating a range of equipment in a makerspace builds students' technical skills. For example, we've seen makerspaces in middle schools start with easy-to-use 3D printers and laser cutters. At the high school level, makerspaces include a greater variety of equipment, such as large format printers and woodworking tools. University makerspaces have more advanced technologies, like multi-color 3D printers, CNC machines, and 3D scanners.
Community-driven makerspaces often include a substantial population of entrepreneurs who utilize shared machine tools to build everything from prototypes to final products to be sold. It is an excellent model to expose students to as they will be exposed to small businesses and the technology used in large-scale manufacturing.
How to Start a Makerspace for Education in New England
Do you want to start a makerspace for education at your New England school or university? Before purchasing equipment, we recommend taking time to go through the following steps to ensure your makerspace is well-used.
Step 1: Define Makerspace Goals
When you start a makerspace, the first step is to define your makerspace goals. To do this, adminstration and instructors who will be using the space should discuss the purpose of the makerspace.
For example, review questions like:
- How will the makerspace enhance our curriculum and institution?
- Who will use the makerspace?
- How can we reach many students with the makerspace?
- What is our vision for the makerspace?
Defining your makerspace goals will get everyone on the same page and ensure that the makerspace will have longevity within the institution for years to come.
Step 2: Design Makerspace Layouts
The next step to starting a makerspace is to design makerspace layouts. You don't need to construct a new building to create a makerspace. We've seen schools get very creative in transforming existing spaces into beautiful makerspaces. Unused campus building spaces, sections of classrooms, and even locker rooms have been transformed into makerspaces in New England.
Makerspace floor plans should encourage exploration, movement, and collaboration. Include equipment appropriate for your students and makerspace goals, along with modular tables and seating. You'll also want to consider storage for smaller tools and consumables.
Stations or designated rooms or areas are very common within makerspaces. As you identify space for your makerspace and create layouts, be mindful of the available electric, plumbing, and HVAC. Some equipment requires special buildouts, including water sources, sinks, ventilation, dust collection, and network access.
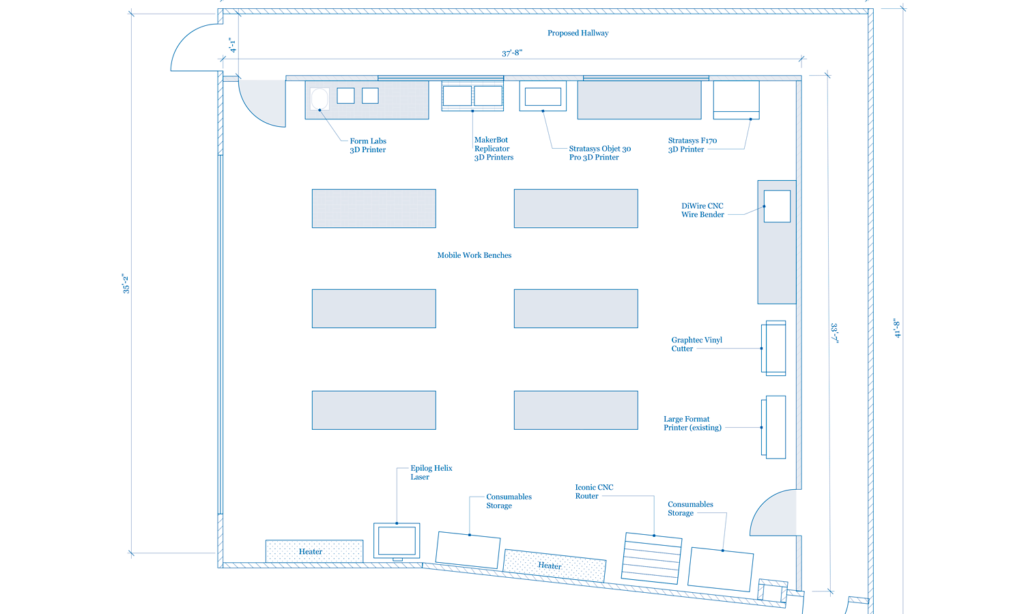
Here are some ideas for your makerspace floor plans:
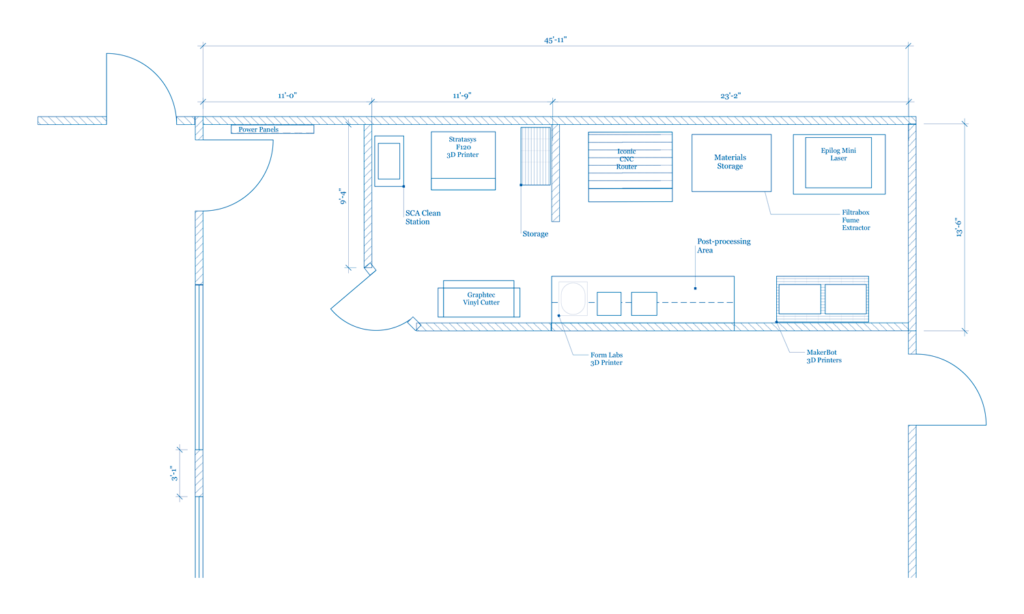
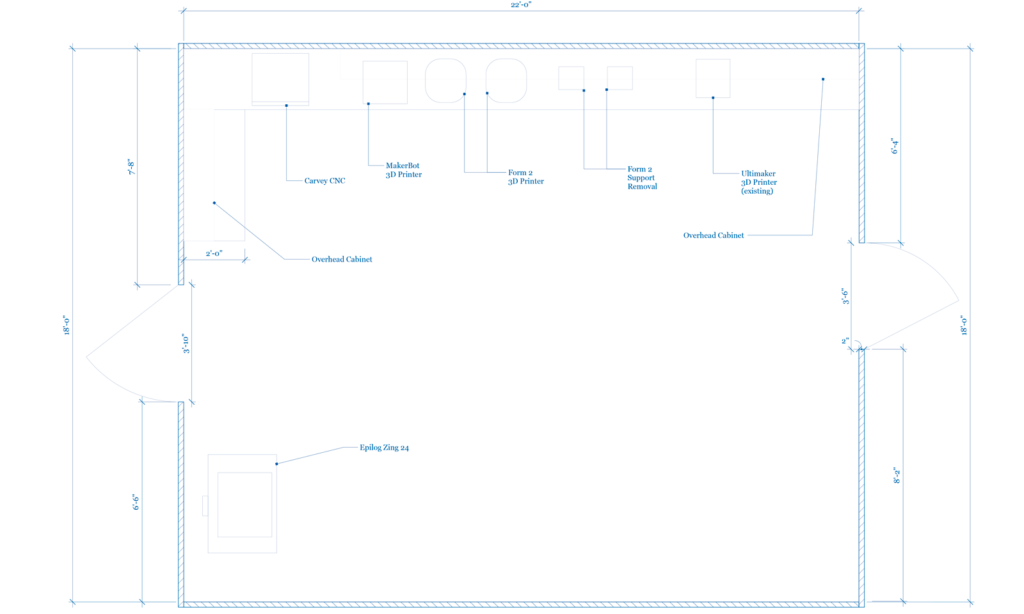
Learn more about beginner makerspaces here.
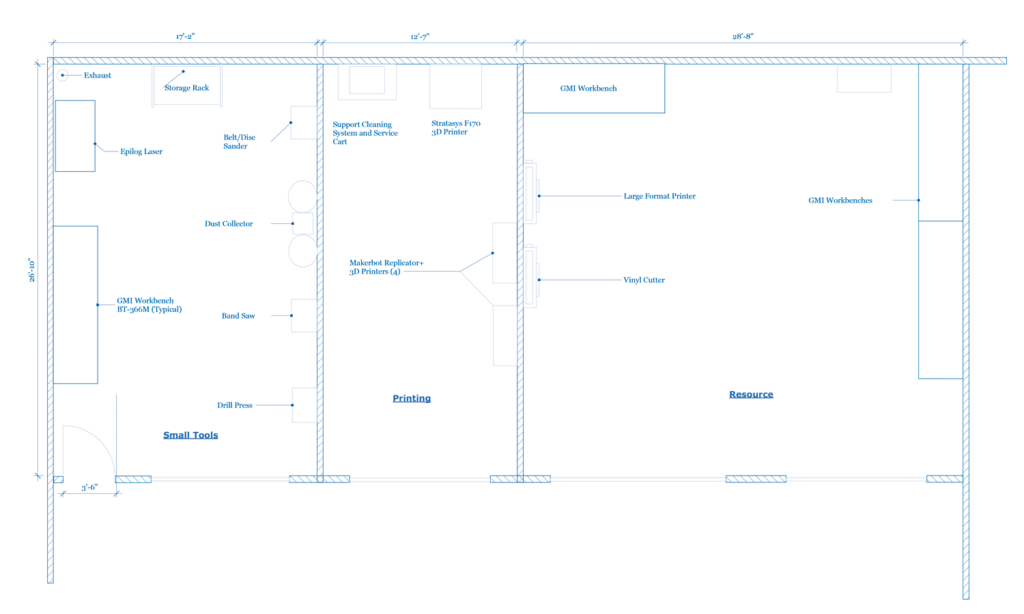
Learn more about intermediate makerspaces here.
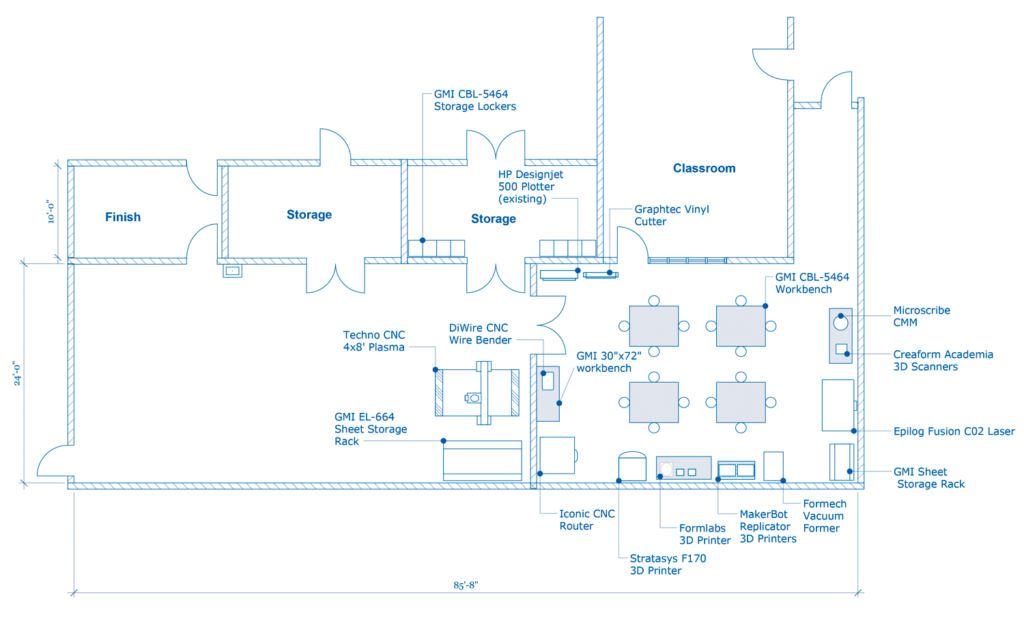
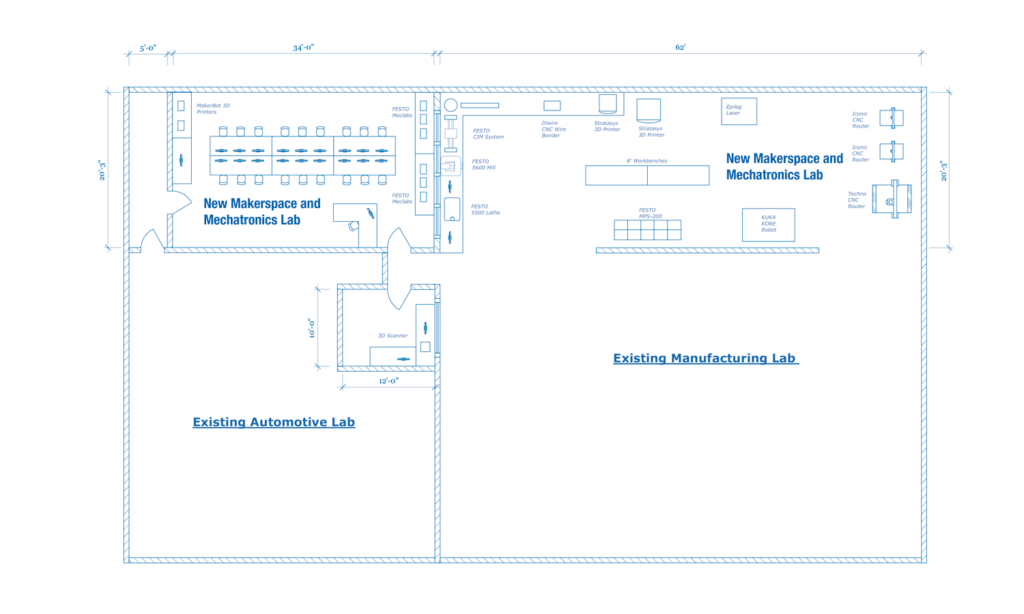
Learn more about advanced makerspaces here.
Step 3: Identify Makerspace Resources
You will need at least one point person for your makerspace. Their responsibilities include:
- Coordinating with instructors
- Helping students with equipment
- Ordering supplies and consumables
- Taking care of equipment maintenance and servicing
University makerspaces have lab directors and managers in charge of makerspaces. In K-12, some schools have salaried staff manage the makerspace and others contract outside personnel.
A strong director has passion for the makerspace, some technical skills, and collaborates well with students and instructors they are supporting.
Makerspace Examples in New England
Do you want a peek at some makerspace examples at schools and universities in New England? Here are some that the AET Labs team is proud to have been a part of:
Fuller Middle School Makerspace in Massachusetts
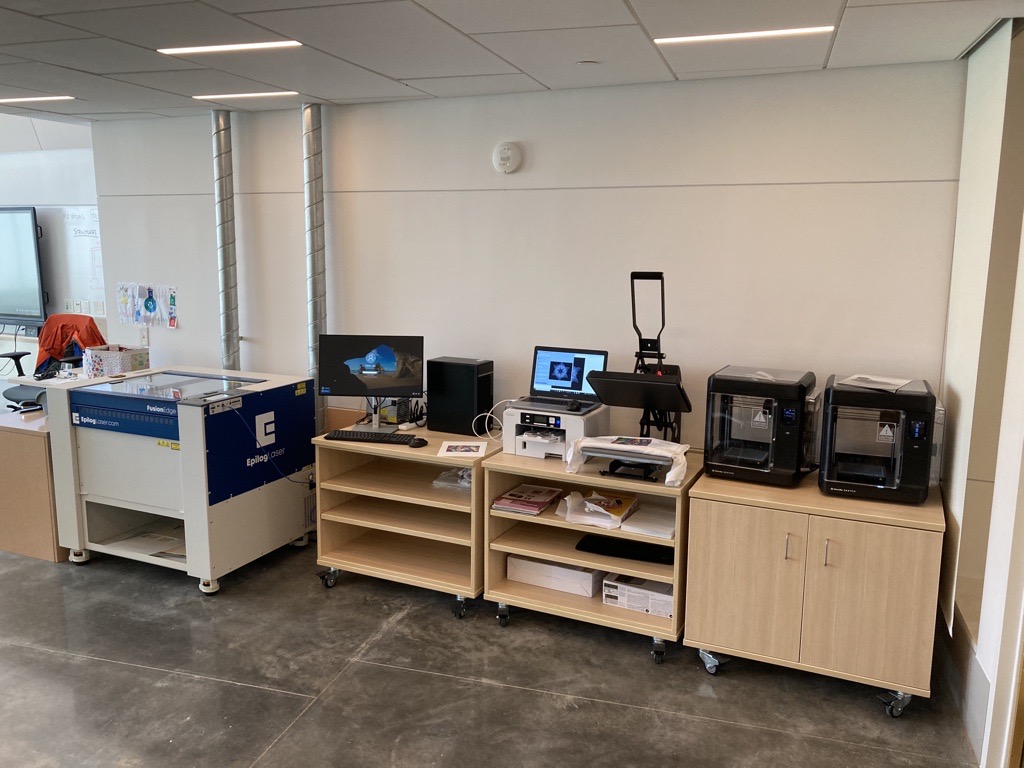

Essex North Shore Agricultural and Technical School Makerspace in Massachusetts
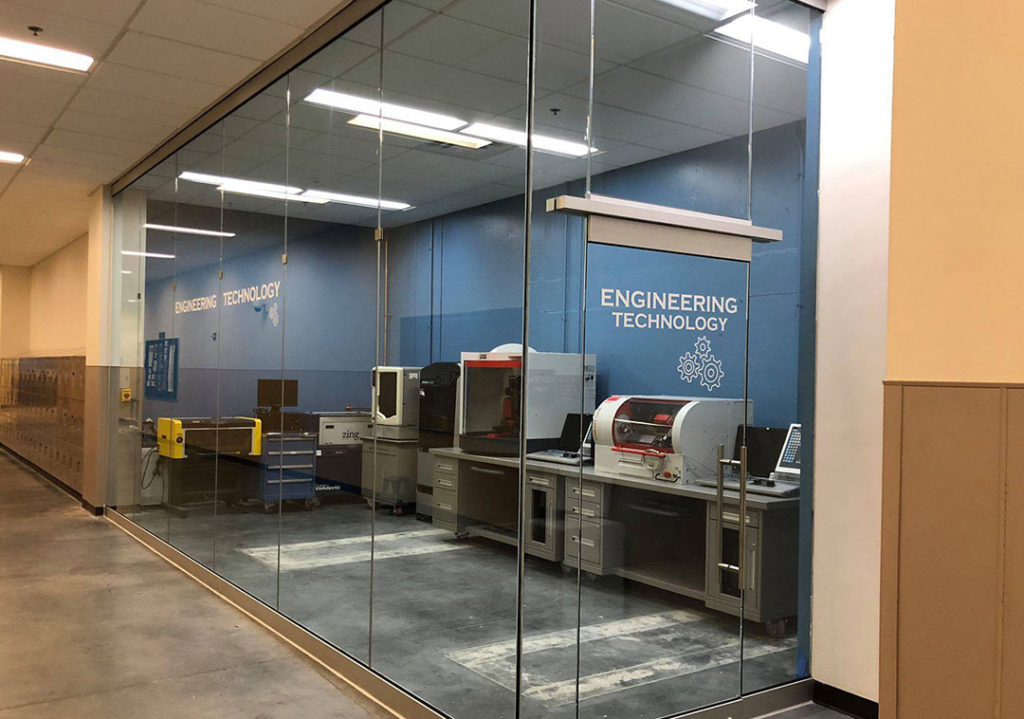

Babson College Makerspace in Massachusetts
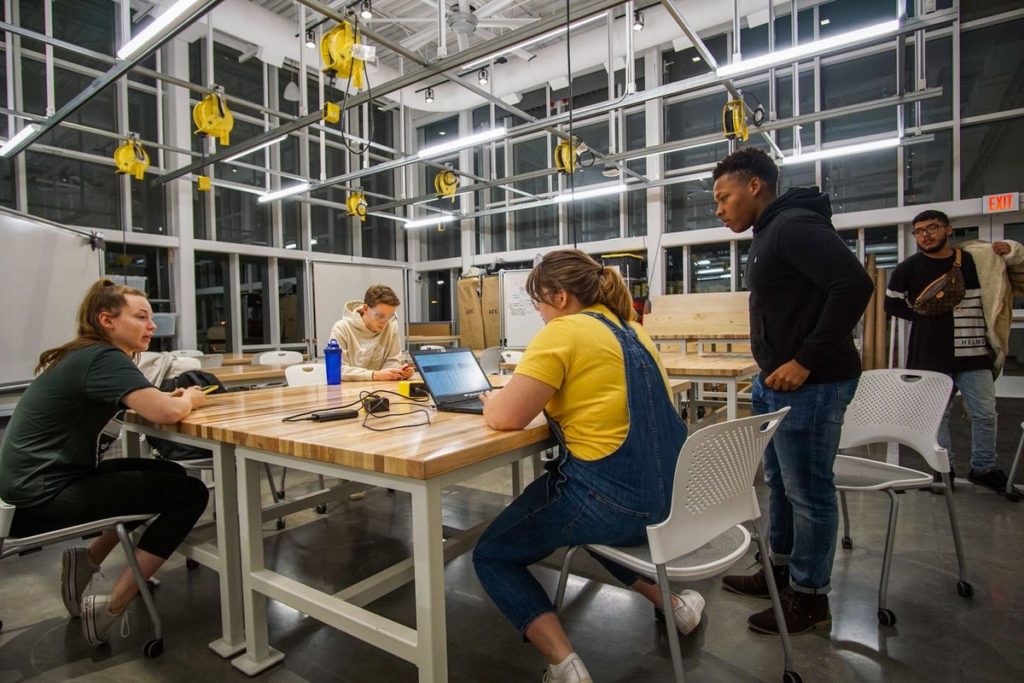

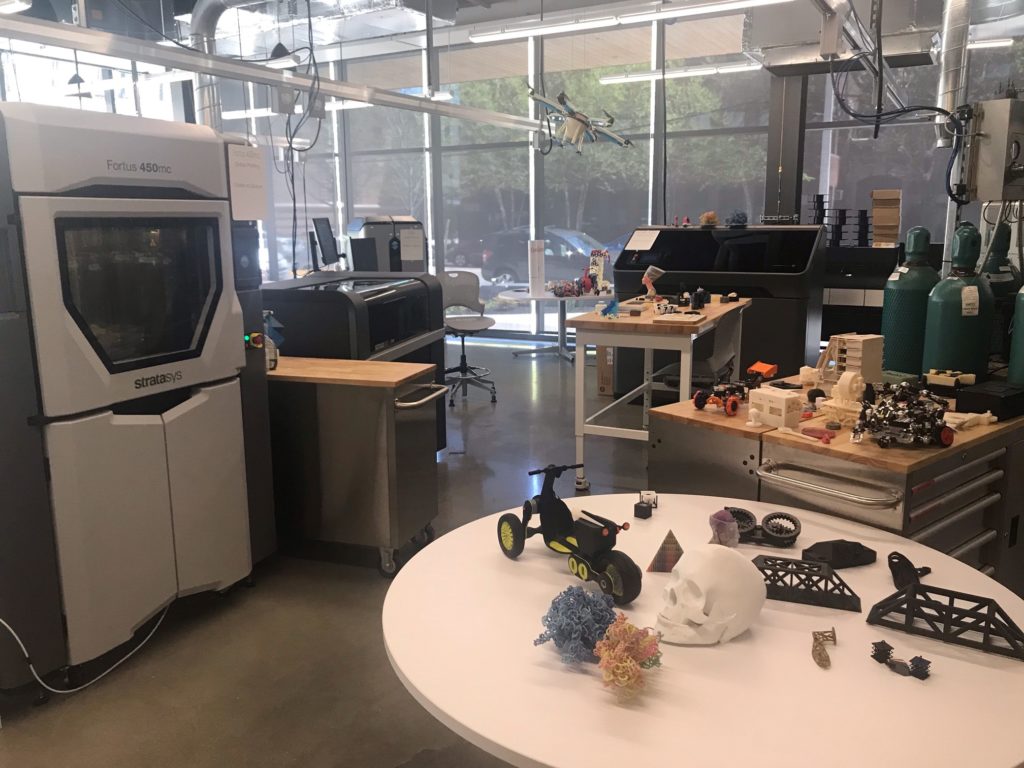
Wentworth Institute of Technology Makerspace in Massachusetts

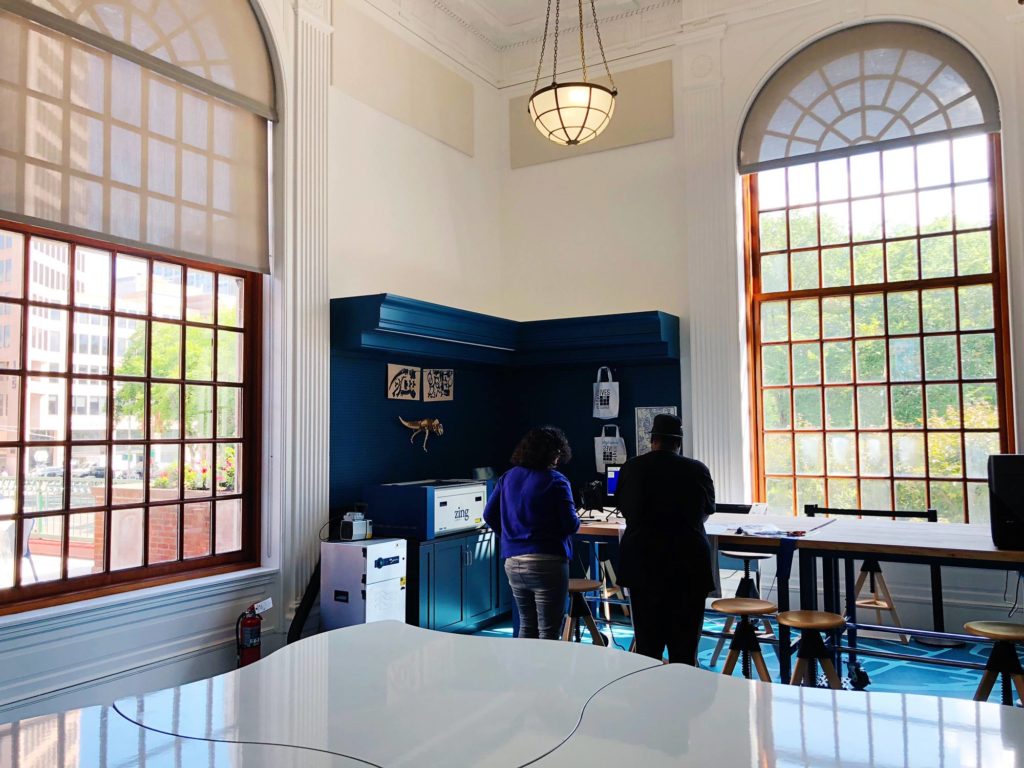
New Haven Free Public Library Makerspace in Connecticut

Makerspaces are a worthwhile pursuit for any school or university to help students gain 21st-century skills and get exposure to equipment used in the industry.
If you're exploring a makerspace for education in New England, AET Labs can help! We specialize in providing end-to-end support for makerspaces in New England. Our services include:
- Helping to establish goals
- Designing makerspace layouts
- Recommending equipment
- Training instructors on equipment
- Installing and servicing equipment


